
Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy editorial process and privacy policy. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2018:chap 20.Ī.D.A.M., Inc. Differential Diagnosis of Common Complaints. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Abnormal uterine bleeding: etiology and management of acute and chronic excessive bleeding. In: Melmed S, Auchus, RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Physiology and pathology of the female reproductive axis. ACOG Committee Opinion No 557: Management of acute abnormal uterine bleeding in nonpregnant reproductive-aged women. PMID: 20027071 .gov/20027071/.Īmerican College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. 110: Noncontraceptive uses of hormonal contraceptives. Procedures to block blood supply to uterine vesselsĪCOG Practice Bulletin No.Tranexamic acid to help treat heavy menstrual bleeding.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen or naproxen) to help control bleeding and reduce menstrual cramps.Other medicines given for AUB may include: The hormones in the IUD are released slowly and may control abnormal bleeding. An IUD is a birth control device that is inserted in the uterus.
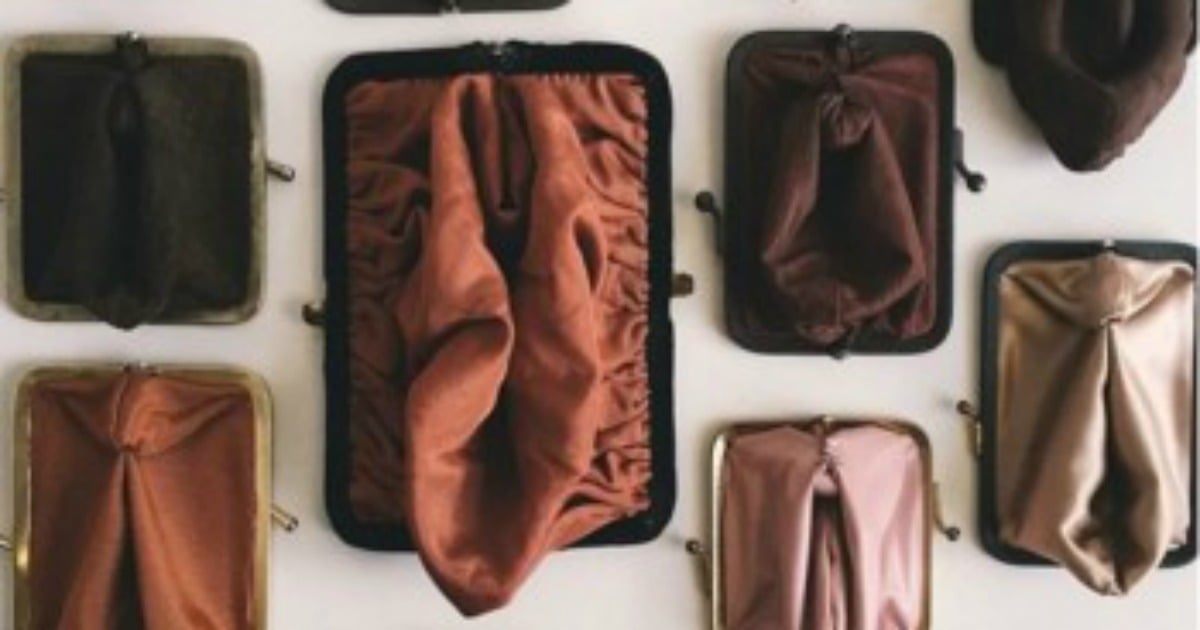
Vagina shapes change because of skin#

Sonohysterography: Fluid is placed in the uterus through a thin tube, while vaginal ultrasound images are made of the uterus.Others may be done at a hospital or surgical center:

Some can be done in your provider's office. Your provider will ask questions about your medical history and symptoms.īased on your symptoms, other tests may be needed. Your provider will perform a physical exam, including a pelvic exam. Effect of low estrogen levels on the vaginal tissue.Use of certain drugs such as blood thinners (Warfarin or Coumadin).Cervical or endometrial biopsy or other procedures.Use of an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control (may cause spotting).Cancer or precancer of the cervix, uterus, ovary, or fallopian tube.Problems with medical conditions may include: Endometrial hyperplasia (thickening or build-up of the lining of the uterus).Injury or disease of the vaginal opening (caused by intercourse, infection, polyp, genital warts, ulcer, or varicose veins).Inflammation or infection of the cervix ( cervicitis).Noncancerous growths in the womb, including uterine fibroids, uterine or cervical polyps, and adenomyosis.Infection in the uterus (pelvic inflammatory disease).Problems with reproductive organs may include: However, talk to your health care provider if you have concerns about the bleeding. Often this is called "breakthrough bleeding." This problem often goes away on its own. Women who take oral contraceptives may experience episodes of abnormal vaginal bleeding. AUB is more common in teenagers and in women who are approaching menopause. Doctors call the problem abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) or anovulatory uterine bleeding. There are many causes of abnormal vaginal bleeding.Ībnormal bleeding is often linked to failure of regular ovulation (anovulation).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
